Between Exchange 2013 and 2016 there where few new operations introduced into EWS, one operation that was introduced was the SetUserPhoto operation which pairs with the GetUserPhoto operation that was introduced in Exchange 2013.
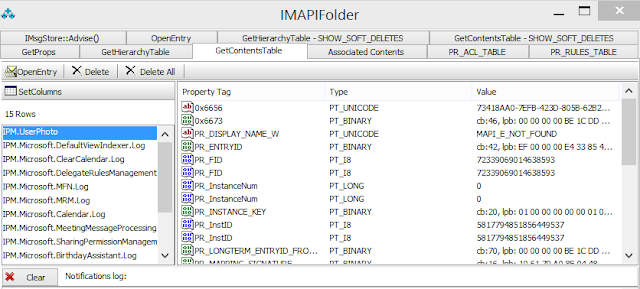
What this operation does is allows you to set/upload a high resolution photo for a user to be used in Exchange and Skype for Business in Exchange Online or Exchange 2016. A little bit more about the high ressolution user photo is that when you set this it uploads this as an item in the Non_IPM_Root of the Mailbox (so it is not visible to the user) with a message class of IPM.UserPhoto if you where to look at a Mailbox with a Mapi Editor you can see the object that this creates. eg
If you look at the UserPhoto Object itself you can see the different size formats are stored ready to access in a number of different Binary Mapi properties eg
So what the SetUserPhoto operation does is handles creating this object and all the different photo formats that applications might require.
Currently there isn't anything in the EWS Managed API to take advantage of this new operation so to use this you can either use the WSDL Proxy Objects (generated against Exchange 2016 or Exchange Online) or just raw soap like the following.
I've put together a Powershell script that use the EWS Managed API to do the discovery and then uses raw soap to do the upload the photo.. I've put this script up on GitHub here https://github.com/gscales/Powershell-Scripts/blob/master/Upload-Photo.ps1
To use this script you use the cmdlet like
Set-PhotoEWS -MailboxName mailbox@domain -Photo c:\temp\photo1.jpg
The script itself looks like
What this operation does is allows you to set/upload a high resolution photo for a user to be used in Exchange and Skype for Business in Exchange Online or Exchange 2016. A little bit more about the high ressolution user photo is that when you set this it uploads this as an item in the Non_IPM_Root of the Mailbox (so it is not visible to the user) with a message class of IPM.UserPhoto if you where to look at a Mailbox with a Mapi Editor you can see the object that this creates. eg
If you look at the UserPhoto Object itself you can see the different size formats are stored ready to access in a number of different Binary Mapi properties eg
So what the SetUserPhoto operation does is handles creating this object and all the different photo formats that applications might require.
Currently there isn't anything in the EWS Managed API to take advantage of this new operation so to use this you can either use the WSDL Proxy Objects (generated against Exchange 2016 or Exchange Online) or just raw soap like the following.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <soap:Header> <RequestServerVersion Version="Exchange2016" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/exchange/services/2006/types" /> </soap:Header> <soap:Body> <SetUserPhoto xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/exchange/services/2006/messages"> <Email>$MailboxName</Email> <Content>$Content</Content> <TypeRequested>UserPhoto</TypeRequested> </SetUserPhoto> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope>
I've put together a Powershell script that use the EWS Managed API to do the discovery and then uses raw soap to do the upload the photo.. I've put this script up on GitHub here https://github.com/gscales/Powershell-Scripts/blob/master/Upload-Photo.ps1
To use this script you use the cmdlet like
Set-PhotoEWS -MailboxName mailbox@domain -Photo c:\temp\photo1.jpg
The script itself looks like
function Connect-Exchange{ param( [Parameter(Position=0, Mandatory=$true)] [string]$MailboxName, [Parameter(Position=1, Mandatory=$true)] [System.Management.Automation.PSCredential]$Credentials, [Parameter(Position=2, Mandatory=$false)] [string]$url ) Begin { Load-EWSManagedAPI ## Set Exchange Version $ExchangeVersion = [Microsoft.Exchange.WebServices.Data.ExchangeVersion]::Exchange2013 ## Create Exchange Service Object $service = New-Object Microsoft.Exchange.WebServices.Data.ExchangeService($ExchangeVersion) ## Set Credentials to use two options are availible Option1 to use explict credentials or Option 2 use the Default (logged On) credentials #Credentials Option 1 using UPN for the windows Account #$psCred = Get-Credential $creds = New-Object System.Net.NetworkCredential($Credentials.UserName.ToString(),$Credentials.GetNetworkCredential().password.ToString()) $service.Credentials = $creds #Credentials Option 2 #service.UseDefaultCredentials = $true #$service.TraceEnabled = $true ## Choose to ignore any SSL Warning issues caused by Self Signed Certificates Handle-SSL ## Set the URL of the CAS (Client Access Server) to use two options are availbe to use Autodiscover to find the CAS URL or Hardcode the CAS to use #CAS URL Option 1 Autodiscover if($url){ $uri=[system.URI] $url $service.Url = $uri } else{ $service.AutodiscoverUrl($MailboxName,{$true}) } Write-host ("Using CAS Server : " + $Service.url) #CAS URL Option 2 Hardcoded #$uri=[system.URI] "https://casservername/ews/exchange.asmx" #$service.Url = $uri ## Optional section for Exchange Impersonation #$service.ImpersonatedUserId = new-object Microsoft.Exchange.WebServices.Data.ImpersonatedUserId([Microsoft.Exchange.WebServices.Data.ConnectingIdType]::SmtpAddress, $MailboxName) if(!$service.URL){ throw "Error connecting to EWS" } else { return $service } } } function Load-EWSManagedAPI{ param( ) Begin { ## Load Managed API dll ###CHECK FOR EWS MANAGED API, IF PRESENT IMPORT THE HIGHEST VERSION EWS DLL, ELSE EXIT $EWSDLL = (($(Get-ItemProperty -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue -Path Registry::$(Get-ChildItem -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue -Path 'Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Exchange\Web Services'|Sort-Object Name -Descending| Select-Object -First 1 -ExpandProperty Name)).'Install Directory') + "Microsoft.Exchange.WebServices.dll") if (Test-Path $EWSDLL) { Import-Module $EWSDLL } else { "$(get-date -format yyyyMMddHHmmss):" "This script requires the EWS Managed API 1.2 or later." "Please download and install the current version of the EWS Managed API from" "http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=255472" "" "Exiting Script." #exit } } } function Handle-SSL{ param( ) Begin { ## Code From http://poshcode.org/624 ## Create a compilation environment $Provider=New-Object Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider $Compiler=$Provider.CreateCompiler() $Params=New-Object System.CodeDom.Compiler.CompilerParameters $Params.GenerateExecutable=$False $Params.GenerateInMemory=$True $Params.IncludeDebugInformation=$False $Params.ReferencedAssemblies.Add("System.DLL") | Out-Null $TASource=@' namespace Local.ToolkitExtensions.Net.CertificatePolicy{ public class TrustAll : System.Net.ICertificatePolicy { public TrustAll() { } public bool CheckValidationResult(System.Net.ServicePoint sp, System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates.X509Certificate cert, System.Net.WebRequest req, int problem) { return true; } } } '@ $TAResults=$Provider.CompileAssemblyFromSource($Params,$TASource) $TAAssembly=$TAResults.CompiledAssembly ## We now create an instance of the TrustAll and attach it to the ServicePointManager $TrustAll=$TAAssembly.CreateInstance("Local.ToolkitExtensions.Net.CertificatePolicy.TrustAll") [System.Net.ServicePointManager]::CertificatePolicy=$TrustAll ## end code from http://poshcode.org/624 } } function Set-PhotoEWS { param( [Parameter(Position=0, Mandatory=$true)] [string]$MailboxName, [Parameter(Mandatory=$true)] [System.Management.Automation.PSCredential]$Credentials, [Parameter(Position=2, Mandatory=$false)] [switch]$useImpersonation, [Parameter(Position=3, Mandatory=$false)] [string]$url, [Parameter(Position=4, Mandatory=$true)] [String]$Photo ) Begin { if($url){ $service = Connect-Exchange -MailboxName $MailboxName -Credentials $Credentials -url $url } else{ $service = Connect-Exchange -MailboxName $MailboxName -Credentials $Credentials } if($useImpersonation.IsPresent){ $service.ImpersonatedUserId = new-object Microsoft.Exchange.WebServices.Data.ImpersonatedUserId([Microsoft.Exchange.WebServices.Data.ConnectingIdType]::SmtpAddress, $MailboxName) } [Byte[]]$FileContent = [System.IO.File]::ReadAllBytes($Photo); $Base64Content = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String($FileContent); $request = Get-SetPhotoRequest -MailboxName $MailboxName -Content $Base64Content $SetPhotoRequest = [System.Net.HttpWebRequest]::Create($service.url.ToString()); $bytes = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetBytes($request); $SetPhotoRequest.ContentLength = $bytes.Length; $SetPhotoRequest.ContentType = "text/xml"; $SetPhotoRequest.UserAgent = "EWS Photo upload"; $SetPhotoRequest.Headers.Add("Translate", "F"); $SetPhotoRequest.Method = "POST"; $SetPhotoRequest.Credentials = New-Object System.Net.NetworkCredential($Credentials.UserName.ToString(),$Credentials.GetNetworkCredential().password.ToString()) $RequestStream = $SetPhotoRequest.GetRequestStream(); $RequestStream.Write($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length); $RequestStream.Close(); $SetPhotoRequest.AllowAutoRedirect = $true; $Response = $SetPhotoRequest.GetResponse().GetResponseStream() $sr = New-Object System.IO.StreamReader($Response) [XML]$xmlReposne = $sr.ReadToEnd() if($xmlReposne.Envelope.Body.SetUserPhotoResponse.ResponseClass -eq "Success"){ Write-Host("Photo Uploaded") } else { Write-Host("Upload failed") Write-Host $sr.ReadToEnd() } } } function Get-SetPhotoRequest { param( [Parameter(Position=0, Mandatory=$true)] [String]$MailboxName, [Parameter(Position=0, Mandatory=$true)] [String]$Content ) Begin { $request = @" <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <soap:Header> <RequestServerVersion Version="Exchange2016" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/exchange/services/2006/types" /> </soap:Header> <soap:Body> <SetUserPhoto xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/exchange/services/2006/messages"> <Email>$MailboxName</Email> <Content>$Content</Content> <TypeRequested>UserPhoto</TypeRequested> </SetUserPhoto> </soap:Body> </soap:Envelope> "@ return $request } }